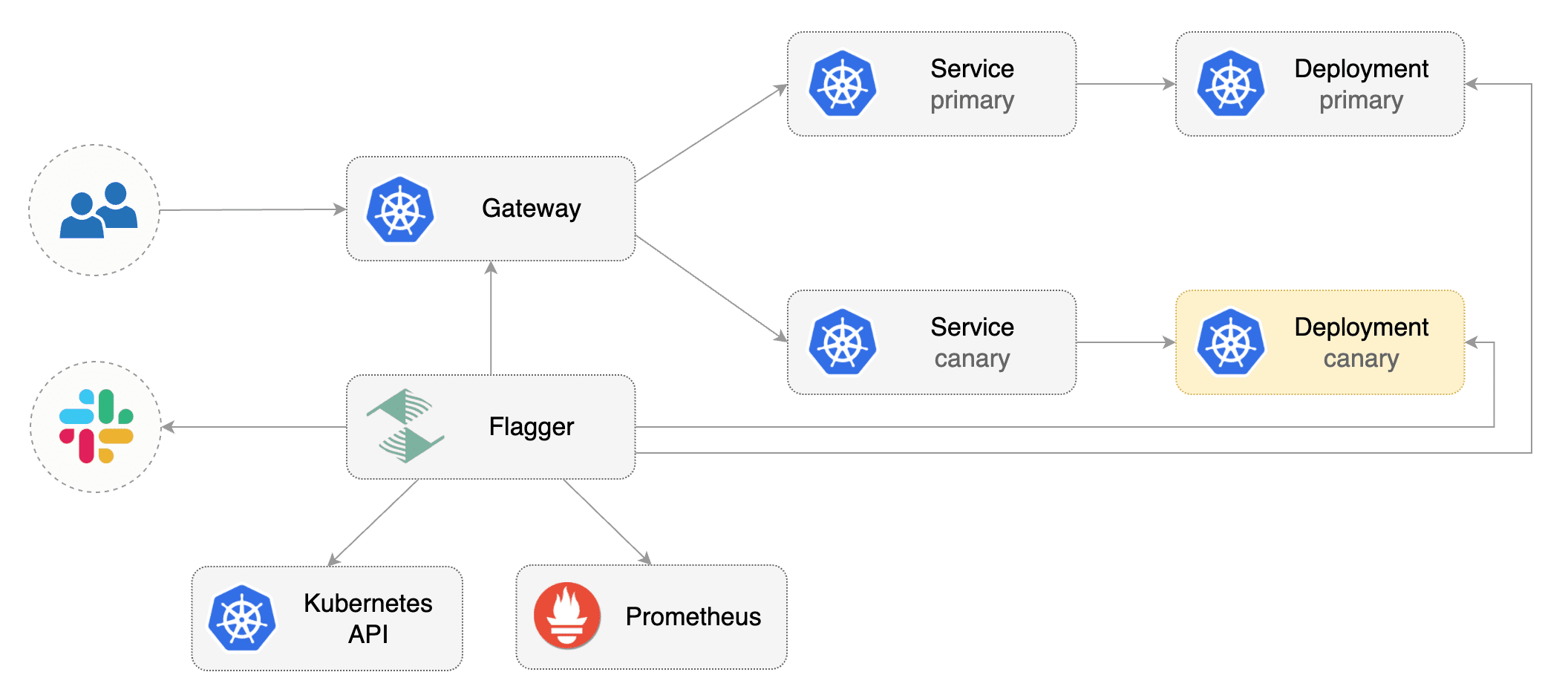
Gateway API Canary Deployments
This guide shows you how to use Gateway API and Flagger to automate canary deployments and A/B testing.
Prerequisites
Flagger requires a Kubernetes cluster v1.16 or newer and any mesh/ingress that implements the v1alpha2 of Gateway API. We’ll be using Contour for the sake of this tutorial, but you can use any other implementation.
Install the GatewayAPI CRDs:
kubectl apply -k github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd?ref=v0.4.1
Install a cluster-wide GatewayClass; a Gateway belonging to the GatewayClass and Contour components in the projectcontour namespace:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcontour/contour/release-1.20/examples/render/contour-gateway.yaml
Install Flagger in the flagger-system namespace:
kubectl apply -k github.com/fluxcd/flagger//kustomize/gatewayapi
Bootstrap
Flagger takes a Kubernetes deployment and optionally a horizontal pod autoscaler (HPA), then creates a series of objects (Kubernetes deployments, ClusterIP services, HTTPRoutes for the Gateway). These objects expose the application inside the mesh and drive the canary analysis and promotion.
Create a test namespace:
kubectl create ns test
Create a deployment and a horizontal pod autoscaler:
kubectl apply -k https://github.com/fluxcd/flagger//kustomize/podinfo?ref=main
Deploy the load testing service to generate traffic during the canary analysis:
kubectl apply -k https://github.com/fluxcd/flagger//kustomize/tester?ref=main
Create metric templates targeting the Prometheus server in the flagger-system namespace. The PromQL queries below are meant for Envoy, but you can
change it to your ingress/mesh provider accordingly.
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1beta1
kind: MetricTemplate
metadata:
name: latency
namespace: flagger-system
spec:
provider:
type: prometheus
address: http://flagger-prometheus:9090
query: |
histogram_quantile(0.99,
sum(
rate(
envoy_cluster_upstream_rq_time_bucket{
envoy_cluster_name=~"{{ namespace }}_{{ target }}-canary_[0-9a-zA-Z-]+",
}[{{ interval }}]
)
) by (le)
)/1000
---
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1beta1
kind: MetricTemplate
metadata:
name: error-rate
namespace: flagger-system
spec:
provider:
type: prometheus
address: http://flagger-prometheus:9090
query: |
100 - sum(
rate(
envoy_cluster_upstream_rq{
envoy_cluster_name=~"{{ namespace }}_{{ target }}-canary_[0-9a-zA-Z-]+",
envoy_response_code!~"5.*"
}[{{ interval }}]
)
)
/
sum(
rate(
envoy_cluster_upstream_rq{
envoy_cluster_name=~"{{ namespace }}_{{ target }}-canary_[0-9a-zA-Z-]+",
}[{{ interval }}]
)
)
* 100
Save the above resource as metric-templates.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f metric-templates.yaml
Create a canary custom resource (replace “loaclproject.contour.io” with your own domain):
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1beta1
kind: Canary
metadata:
name: podinfo
namespace: test
spec:
# deployment reference
targetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: podinfo
# the maximum time in seconds for the canary deployment
# to make progress before it is rollback (default 600s)
progressDeadlineSeconds: 60
# HPA reference (optional)
autoscalerRef:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
name: podinfo
service:
# service port number
port: 9898
# container port number or name (optional)
targetPort: 9898
# Gateway API HTTPRoute host names
hosts:
- localproject.contour.io
# Reference to the Gateway that the generated HTTPRoute would attach to.
gatewayRefs:
- name: contour
namespace: projectcontour
analysis:
# schedule interval (default 60s)
interval: 1m
# max number of failed metric checks before rollback
threshold: 5
# max traffic percentage routed to canary
# percentage (0-100)
maxWeight: 50
# canary increment step
# percentage (0-100)
stepWeight: 10
metrics:
- name: error-rate
# max error rate (5xx responses)
# percentage (0-100)
templateRef:
name: error-rate
namespace: flagger-system
thresholdRange:
max: 1
interval: 1m
- name: latency
templateRef:
name: latency
namespace: flagger-system
# seconds
thresholdRange:
max: 0.5
interval: 30s
# testing (optional)
webhooks:
- name: smoke-test
type: pre-rollout
url: http://flagger-loadtester.test/
timeout: 15s
metadata:
type: bash
cmd: "curl -sd 'anon' http://podinfo-canary.test:9898/token | grep token"
- name: load-test
url: http://flagger-loadtester.test/
timeout: 5s
metadata:
cmd: "hey -z 2m -q 10 -c 2 -host localproject.contour.io http://envoy.projectcontour/"
Save the above resource as podinfo-canary.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./podinfo-canary.yaml
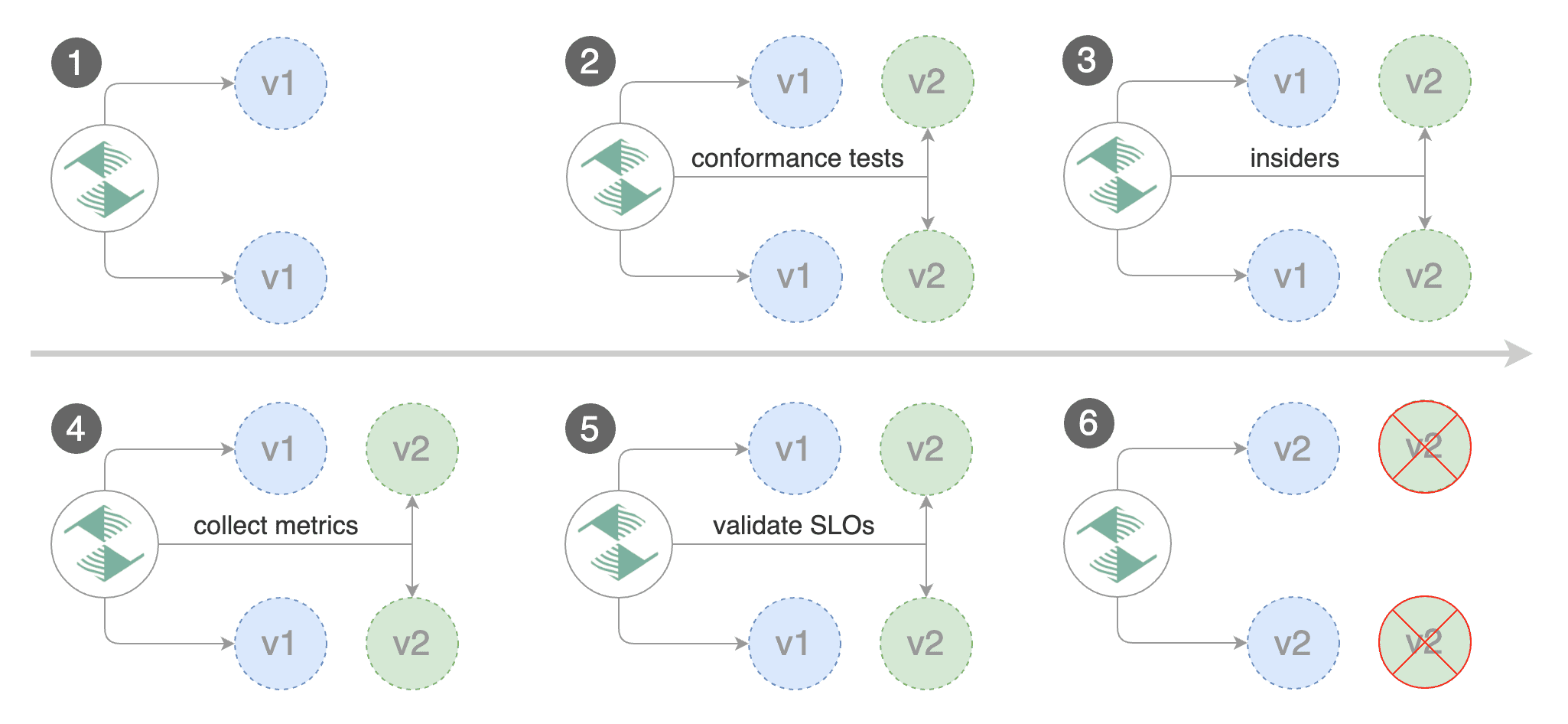
When the canary analysis starts, Flagger will call the pre-rollout webhooks before routing traffic to the canary. The canary analysis will run for five minutes while validating the HTTP metrics and rollout hooks every minute.
After a couple of seconds Flagger will create the canary objects:
# applied
deployment.apps/podinfo
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/podinfo
canary.flagger.app/podinfo
# generated
deployment.apps/podinfo-primary
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/podinfo-primary
service/podinfo
service/podinfo-canary
service/podinfo-primary
httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io/podinfo
Expose the app outside the cluster
Find the external address of Contour’s Envoy load balancer:
export ADDRESS="$(kubectl -n projectcontour get svc/envoy -ojson \
| jq -r ".status.loadBalancer.ingress[].hostname")"
echo $ADDRESS
Configure your DNS server with a CNAME record (AWS) or A record (GKE/AKS/DOKS) and point a domain e.g. localproject.contour.io to the LB address.
Now you can access the podinfo UI using your domain address.
Note that you should be using HTTPS when exposing production workloads on internet. You can obtain free TLS certs from Let’s Encrypt, read this guide on how to configure cert-manager to secure Contour with TLS certificates.
If you’re using a local cluster via kind/k3s you can port forward the Envoy LoadBalancer service:
kubectl port-forward -n projectcontour svc/envoy 8080:80
Now you can access podinfo via curl -H "Host: localproject.contour.io" localhost:8080
Automated canary promotion
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image:
kubectl -n test set image deployment/podinfo \
podinfod=stefanprodan/podinfo:6.0.1
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout:
kubectl -n test describe canary/podinfo
Status:
Canary Weight: 0
Failed Checks: 0
Phase: Succeeded
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Synced 3m flagger New revision detected podinfo.test
Normal Synced 3m flagger Scaling up podinfo.test
Warning Synced 3m flagger Waiting for podinfo.test rollout to finish: 0 of 1 updated replicas are available
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 5
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 10
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 15
Normal Synced 2m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 20
Normal Synced 2m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 25
Normal Synced 1m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 30
Normal Synced 1m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 35
Normal Synced 55s flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 40
Normal Synced 45s flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 45
Normal Synced 35s flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 50
Normal Synced 25s flagger Copying podinfo.test template spec to podinfo-primary.test
Warning Synced 15s flagger Waiting for podinfo-primary.test rollout to finish: 1 of 2 updated replicas are available
Normal Synced 5s flagger Promotion completed! Scaling down podinfo.test
Note that if you apply new changes to the deployment during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
A canary deployment is triggered by changes in any of the following objects:
- Deployment PodSpec (container image, command, ports, env, resources, etc)
- ConfigMaps mounted as volumes or mapped to environment variables
- Secrets mounted as volumes or mapped to environment variables
You can monitor how Flagger progressively changes the weights of the HTTPRoute object that is attahed to the Gateway with:
watch kubectl get httproute -n test podinfo -o=jsonpath='{.spec.rules}'
You can monitor all canaries with:
watch kubectl get canaries --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME STATUS WEIGHT LASTTRANSITIONTIME
test podinfo Progressing 15 2022-01-16T14:05:07Z
prod frontend Succeeded 0 2022-01-15T16:15:07Z
prod backend Failed 0 2022-01-14T17:05:07Z
Automated rollback
During the canary analysis you can generate HTTP 500 errors and high latency to test if Flagger pauses the rollout.
Trigger another canary deployment:
kubectl -n test set image deployment/podinfo \
podinfod=stefanprodan/podinfo:6.0.2
Exec into the load tester pod with:
kubectl -n test exec -it flagger-loadtester-xx-xx sh
Generate HTTP 500 errors:
watch curl http://podinfo-canary:9898/status/500
Generate latency:
watch curl http://podinfo-canary:9898/delay/1
When the number of failed checks reaches the canary analysis threshold, the traffic is routed back to the primary, the canary is scaled to zero and the rollout is marked as failed.
kubectl -n test describe canary/podinfo
Status:
Canary Weight: 0
Failed Checks: 10
Phase: Failed
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Synced 3m flagger Starting canary deployment for podinfo.test
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 5
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 10
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary weight 15
Normal Synced 3m flagger Halt podinfo.test advancement error rate 69.17% > 1%
Normal Synced 2m flagger Halt podinfo.test advancement error rate 61.39% > 1%
Normal Synced 2m flagger Halt podinfo.test advancement error rate 55.06% > 1%
Normal Synced 2m flagger Halt podinfo.test advancement error rate 47.00% > 1%
Normal Synced 2m flagger (combined from similar events): Halt podinfo.test advancement error rate 38.08% > 1%
Warning Synced 1m flagger Rolling back podinfo.test failed checks threshold reached 10
Warning Synced 1m flagger Canary failed! Scaling down podinfo.test
A/B Testing
Besides weighted routing, Flagger can be configured to route traffic to the canary based on HTTP match conditions. In an A/B testing scenario, you’ll be using HTTP headers or cookies to target a certain segment of your users. This is particularly useful for frontend applications that require session affinity.
Create a canary custom resource (replace “loaclproject.contour.io” with your own domain):
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1beta1
kind: Canary
metadata:
name: podinfo
namespace: test
spec:
# deployment reference
targetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: podinfo
# the maximum time in seconds for the canary deployment
# to make progress before it is rollback (default 600s)
progressDeadlineSeconds: 60
# HPA reference (optional)
autoscalerRef:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
name: podinfo
service:
# service port number
port: 9898
# container port number or name (optional)
targetPort: 9898
# Gateway API HTTPRoute host names
hosts:
- localproject.contour.io
# Reference to the Gateway that the generated HTTPRoute would attach to.
gatewayRefs:
- name: contour
namespace: projectcontour
analysis:
# schedule interval (default 60s)
interval: 1m
# max number of failed metric checks before rollback
threshold: 5
# max traffic percentage routed to canary
# percentage (0-100)
maxWeight: 50
# canary increment step
# percentage (0-100)
stepWeight: 10
metrics:
- name: error-rate
# max error rate (5xx responses)
# percentage (0-100)
templateRef:
name: error-rate
namespace: flagger-system
thresholdRange:
max: 1
interval: 1m
- name: latency
templateRef:
name: latency
namespace: flagger-system
# seconds
thresholdRange:
max: 0.5
interval: 30s
# testing (optional)
webhooks:
- name: smoke-test
type: pre-rollout
url: http://flagger-loadtester.test/
timeout: 15s
metadata:
type: bash
cmd: "curl -sd 'anon' http://podinfo-canary.test:9898/token | grep token"
- name: load-test
url: http://flagger-loadtester.test/
timeout: 5s
metadata:
cmd: "hey -z 2m -q 10 -c 2 -host localproject.contour.io -H 'X-Canary: insider' http://envoy.projectcontour/"
The above configuration will run an analysis for ten minutes targeting those users that have an insider cookie.
Save the above resource as podinfo-ab-canary.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./podinfo-ab-canary.yaml
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image:
kubectl -n test set image deployment/podinfo \
podinfod=stefanprodan/podinfo:6.0.3
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout:
kubectl -n test describe canary/abtest
Status:
Failed Checks: 0
Phase: Succeeded
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Synced 3m flagger New revision detected podinfo.test
Normal Synced 3m flagger Scaling up podinfo.test
Warning Synced 3m flagger Waiting for podinfo.test rollout to finish: 0 of 1 updated replicas are available
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 1/10
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 2/10
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 3/10
Normal Synced 2m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 4/10
Normal Synced 2m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 5/10
Normal Synced 1m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 6/10
Normal Synced 1m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 7/10
Normal Synced 55s flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 8/10
Normal Synced 45s flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 9/10
Normal Synced 35s flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 10/10
Normal Synced 25s flagger Copying podinfo.test template spec to podinfo-primary.test
Warning Synced 15s flagger Waiting for podinfo-primary.test rollout to finish: 1 of 2 updated replicas are available
Normal Synced 5s flagger Promotion completed! Scaling down podinfo.test
The above procedures can be extended with custom metrics checks, webhooks, manual promotion approval and Slack or MS Teams notifications.