Troubleshooting cheatsheet
Getting basic information
Show all Flux objects that are not ready
flux get all -A --status-selector ready=false
Show flux warning events
kubectl get events -n flux-system --field-selector type=Warning
Flux CLI (check for Ready=True and Suspend=False)
flux get sources all -A
See the CLI reference for
get_sources_all.
kubectl (check for Ready=True)
kubectl get gitrepositories.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A
kubectl get helmrepositories.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A
Flux CLI (check for Ready=True and Suspend=False)
flux get kustomizations -A
flux get helmreleases -A
CLI reference for
get_kustomizations and
get_helmreleases.
kubectl (check for Ready=True)
kubectl get kustomizations.kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A
kubectl get helmreleases.helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A
kubectl get helmcharts.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A
HelmCharts and HelmReleases CRDs conflict with other Helm controllers
When a HelmRelease exhibits the issue HelmChart 'podinfo/podinfo-podinfo' is not ready, a common issue on k3s clusters or other environments that bundle a different Helm controller is caused by a conflict between these CRDs when they are used without fully qualifying.
For example: kubectl get helmcharts can access the wrong CRD and users may be fooled into thinking that a HelmChart resource was not created successfully. To avoid this issue, use the alternative flux get source chart or fully qualify when using kubectl get as shown above.
Looking for controller errors:
flux logs --all-namespaces --level=error
Check controllers readiness and versions:
flux check
CLI reference for
check.
Changes not being applied
- Are the sources up-to-date and ready?
How to check:
- Grafana Dashboard - Flux Cluster Stats
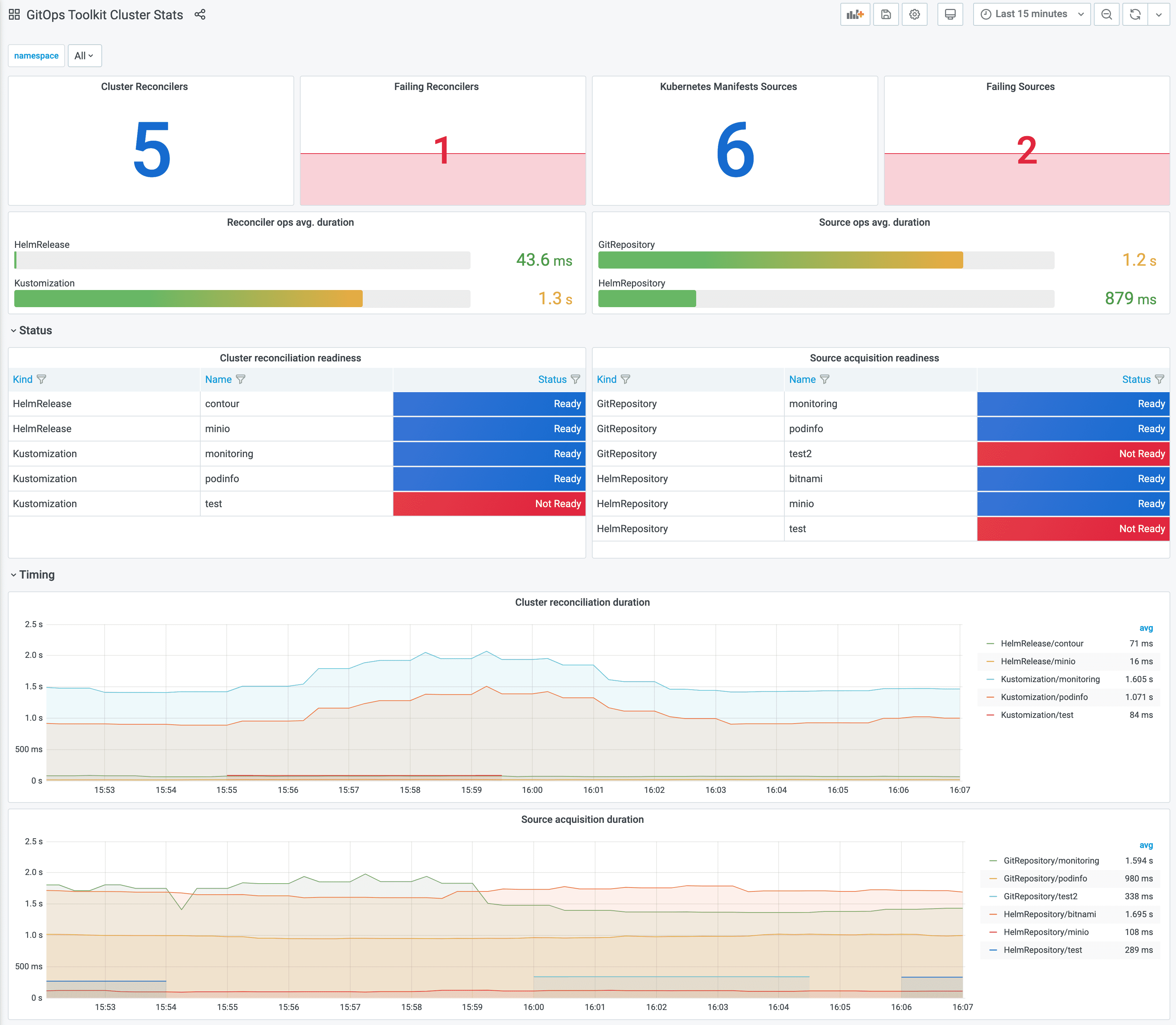
- Flux CLI (check for
Ready=TrueandSuspend=False)
See the CLI reference forflux get sources all -Aget_sources_all. kubectl(check forReady=True)kubectl get gitrepositories.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A kubectl get helmrepositories.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A
- Grafana Dashboard - Flux Cluster Stats
Kustomization/HelmReleasesconfigured and ready? How to check:- Grafana Dashboard - Flux Cluster Stats
- Flux CLI (check for
Ready=TrueandSuspend=False)
CLI reference forflux get kustomizations -A flux get helmreleases -Aget_kustomizationsandget_helmreleases. kubectl(check forReady=True)kubectl get kustomizations.kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A kubectl get helmreleases.helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A kubectl get helmcharts.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io -A
Kustomize-related issues
How do I resolve webhook does not support dry run errors?
If you’ve installed Kubernetes dynamic admission controls you may see Flux
failing to reconcile with an error similar to
dry-run failed, error: admission webhook "validation-service.default.svc" does not support dry run.
To fix this issue, you’ll have to find the ValidatingWebhookConfiguration or the MutatingWebhookConfiguration,
and set the sideEffects to None or NoneOnDryRun:
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
sideEffects: None
How do I resolve some/resource configured events spam?
If the controller emits change events for a specific resource (even if the resource hasn’t changed),
you’ll need to edit your YAML manifests and remove any optional field that is set to null,
empty string or empty object.
Example of empty fields that will trigger drift events:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Example
metadata:
name: example
spec:
field1: null
field2: {}
field3: []
field4:
The kustomize-controller detects drift between the manifests and the in-cluster resources by running a server-side apply dry-run, removing the empty fields from your manifests will help the controller detect drift correctly.
Helm-related issues
How do I resolve a Request entity too large: limit is 3145728 error during Helm install or upgrade?
This error is returned by Helm when the release that is attempted to be made does not fit in a
Secret. Most of the time this is due to exceptionally large (umbrella) charts, as explained
in
helm/helm#8281.
If you are running into this, confirm first that your chart has all the required excludes in
their respective
.helmignore and
.sourceignore files.
How to debug “not ready” errors?
Misconfiguring the HelmRelease.spec.chart, like a typo in the chart name, version or chart source URL
would result in a “HelmChart is not ready” error displayed by:
$ flux get helmreleases --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY MESSAGE
default podinfo False HelmChart 'default/default-podinfo' is not ready
In order to get to the root cause, first make sure the source e.g. the HelmRepository
is configured properly and has access to the remote index.yaml:
$ flux get sources helm --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY MESSAGE
default podinfo False failed to fetch https://stefanprodan.github.io/podinfo2/index.yaml : 404 Not Found
If the source is Ready, then the error must be caused by the chart,
for example due to an invalid chart name or non-existing version:
$ flux get sources chart --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY MESSAGE
default default-podinfo False no chart version found for podinfo-9.0.0
How to debug “install retries exhausted” errors?
By default, Flux performs a health check of all the Kubernetes resources created at install time.
If any resource fails to become ready after five minutes, the HelmRelease will be marked as not ready:
$ flux get helmreleases --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY MESSAGE
default podinfo False install retries exhausted
To find the resource that caused the installation failure, you can print the events of the Helm release with:
$ kubectl describe helmrelease podinfo -n default
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal info 2m23s helm-controller Helm install has started
Normal error 82s helm-controller Helm install failed: timed out waiting for the condition
Last Helm logs:
creating 4 resource(s)
beginning wait for 4 resources with timeout of 5m0s
Deployment is not ready: default/podinfo. 0 out of 1 expected pods are ready
To inspect the failing resources, you can disable the health checks with:
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: podinfo
namespace: default
spec:
install:
disableWait: true
upgrade:
disableWait: true
With disableWait: true, Flux will no longer wait for the resources to become ready, so you can
inspect the deployment and find the underlying issue e.g. kubectl describe deployment podinfo.
Raspberry Pi related issues
How do I resolve a unable to open the Badger database that puts image-reflector-controller in CrashLoopBackOff?
This error is commonly found in low-memory environments where an Out Of Memory condition is likely to be experienced, like on Raspberry Pi 2 and 3 boards which have only 1GB of RAM each.
If you are on Raspbian, the default size of 100MB swap file is not large enough to avoid the fault
condition, and can be updated through configuration in /etc/dphys-swapfile:
add at least 1GB swap.